Quadratic Constrained Quadratic Programming problem
scs-eigen can be used to solve Quadratic Constrained Quadratic Programming (QCQP) problems in the for
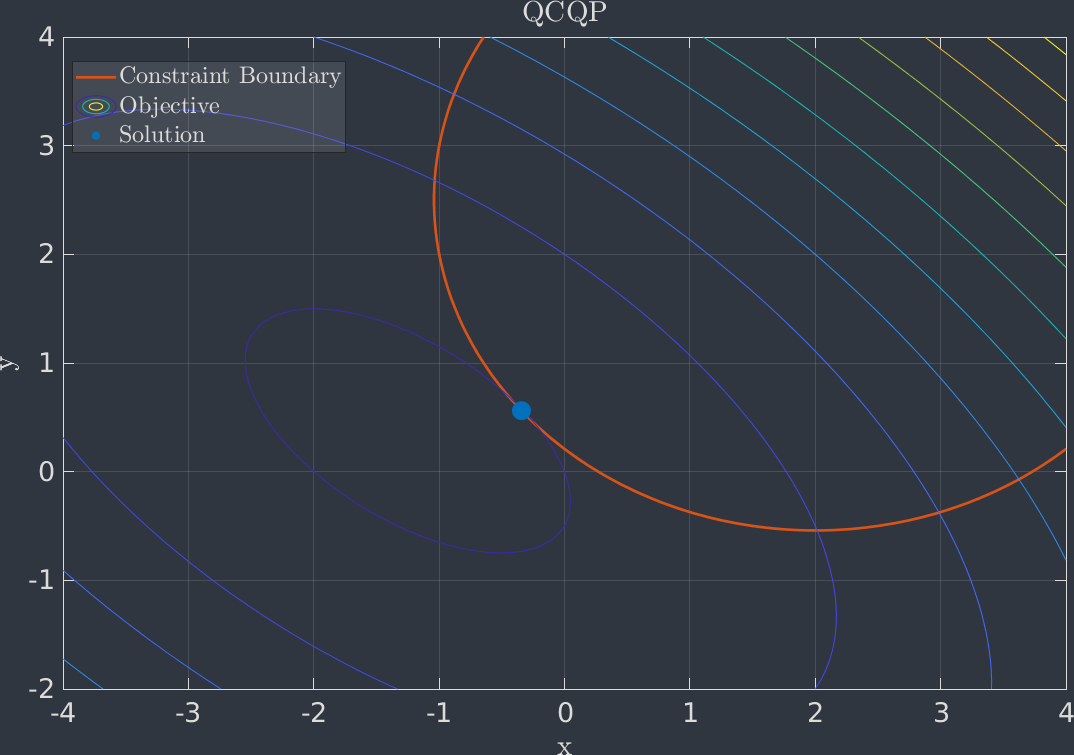
where is the optimization variable. The objective function is defined by a positive semidefinite matrix and vector . The quadratic constraints are defined positive semidefinite matrices and vectors .
The following example shows how scs-eigen can be used to solve the QCQP problem:
First of all you should include ScsEigen
#include <ScsEigen/ScsEigen.h>
You can also define the Hessian, gradient the constraint matrix and vectors.
Eigen::Matrix2d H; H << 3, 2, 2, 4; Eigen::Vector2d gradient; gradient << 3, 1; Eigen::Matrix2d A = 2 * Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity(); Eigen::Vector2d b; b << -4, -5; double upperBound = -1;
Once the matrices used to described the QCQP problem have been defined you can create ScsEigen:: and initialize the number of variables.
ScsEigen::Solver solver; solver.setNumberOfVariabels(2);
Now you can set the constraints and the cost using ScsEigen:: class
solver.mathematicalProgram().addQuadraticConstraint( std::make_shared<ScsEigen::QuadraticConstraint>(A, b, upperBound), "quadratic constraint"); solver.mathematicalProgram().addQuadraticCost( std::make_shared<ScsEigen::QuadraticCost>(H, gradient), "quadratic cost");
You can finally solve the problem and get the solution
solver.solve(); Eigen::Vector2d solution = solver.solution().solution;
The complete example follows
### CMakeLists.txt project(QCQP) find_package(ScsEigen REQUIRED) add_executable(QCQP qcqp.cpp) target_link_libraries(QCQP ScsEigen::ScsEigen)
/// qp.cpp #include <ScsEigen/ScsEigen.h> #include <Eigen/Dense> int main() { Eigen::Matrix2d H; H << 3, 2, 2, 4; Eigen::Vector2d gradient; gradient << 3, 1; Eigen::Matrix2d A = 2 * Eigen::Matrix2d::Identity(); Eigen::Vector2d b; b << -4, -5; ScsEigen::Solver solver; solver.mathematicalProgram().setNumberOVfariables(2); if (!solver.mathematicalProgram().addQuadraticCost( std::make_shared<ScsEigen::QuadraticCost>(H, gradient), "quadratic cost")) return EXIT_FAILURE; if (!solver.mathematicalProgram().addQuadraticConstraint( // std::make_shared<ScsEigen::QuadraticConstraint>(A, b, upperBound), "quadratic constraint")) return EXIT_FAILURE; if (!solver.solve()) return EXIT_FAILURE; if (!solver.solution().isValid()) return EXIT_FAILURE; if (solver.solution().status != ScsEigen::Solution::Status::solved) return EXIT_FAILURE; Eigen::Vector2d solution = solver.solution().solution; return EXIT_SUCCESS; }